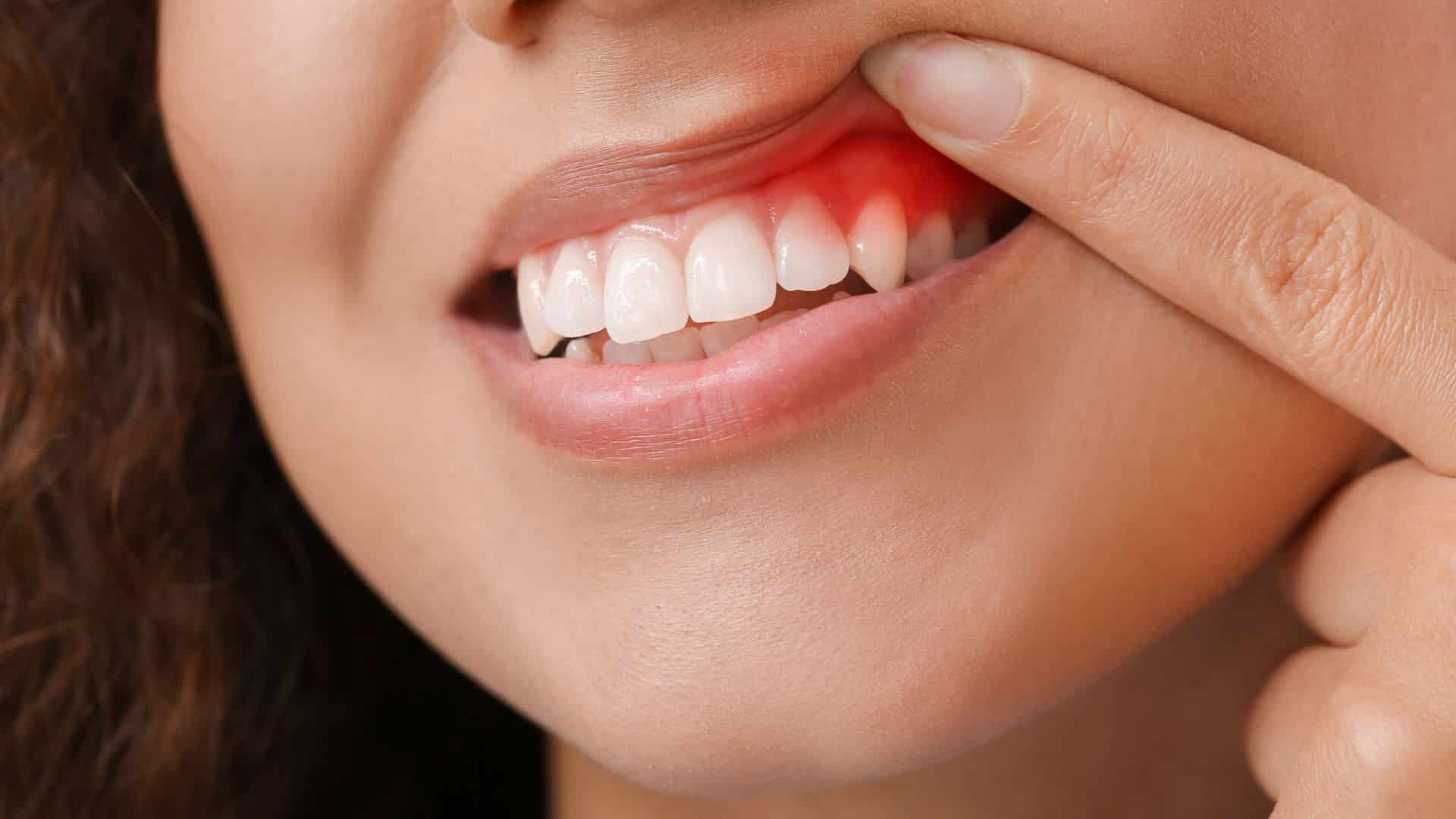
Cautionary Tale: Treating Gum Disease at Home Can Be Risky
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent oral health issue affecting millions globally. While maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for prevention, gum disease often requires professional dental intervention for treatment. This article explores the reasons why attempting to cure gum disease entirely at home can be risky and explores alternative approaches to support gum health alongside seeking professional care.
The Importance of Professional Dental Care:
Gum disease progresses in stages, ranging from mild gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) to advanced periodontitis (bone loss around the teeth). Early intervention is critical to prevent gum disease from progressing and potentially leading to tooth loss. Here’s why a dentist’s expertise is invaluable:
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning: A dentist can accurately diagnose the stage of gum disease and develop a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs. This might involve scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotic therapy, or even surgery in severe cases.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This professional cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar buildup above and below the gum line, which is often difficult to achieve effectively at home.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular dental checkups allow your dentist to monitor your gum health, identify any potential issues early on, and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
Why DIY Cures for Gum Disease are Unreliable:
While some natural remedies might offer temporary relief from gum disease symptoms, they cannot replace professional dental care for several reasons:
- Limited Effectiveness: Natural remedies like salt water rinses or herbal mouthwashes may help reduce inflammation, but they cannot remove plaque and tartar buildup effectively, the root cause of gum disease.
- Risk of Delaying Treatment: Relying solely on home remedies can delay seeking essential professional treatment, allowing gum disease to progress and potentially leading to more severe complications.
- Underlying Causes: Gum disease can sometimes be linked to underlying medical conditions like diabetes. A dentist can identify such connections and recommend appropriate treatment.
Safe and Effective Strategies to Support Gum Health:
While professional dental care is paramount, there are steps you can take at home to support healthy gums alongside your dentist’s recommendations:
- Brushing and Flossing: Meticulous brushing twice a day for two minutes and flossing daily are essential to remove plaque and prevent its buildup. Pay particular attention to the gum line.
- Antibacterial Toothpaste and Mouthwash: Consider using an ADA-approved toothpaste and mouthwash containing fluoride and antibacterial ingredients to combat plaque and freshen breath.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for overall oral health. Limit sugary foods that promote plaque buildup.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum disease. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your oral health.
Early Detection and Intervention is Key:
Regular dental checkups are crucial for early detection of gum disease. Here are some signs that warrant a dentist visit:
- Bleeding Gums: Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing is a common sign of gum inflammation.
- Red and Swollen Gums: Healthy gums should appear pink and firm. Redness and swelling can indicate gingivitis.
- Receding Gums: Gums pulling away from the teeth expose the tooth root and can be a sign of advanced gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath (halitosis) can be a symptom of gum disease.
- Loose Teeth: Loose teeth are a severe indicator of advanced gum disease and bone loss around the teeth.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies for Gum Health (Alongside Professional Care)
While professional dental care remains the cornerstone of gum disease treatment, some complementary therapies can be explored alongside your dentist’s recommendations to support gum health. It’s crucial to remember that these are not substitutes for professional treatment but rather additional strategies to consider:
-
Oil Pulling: This ancient practice involves swishing oil (coconut oil is commonly used) in your mouth for 15-20 minutes before spitting it out. Proponents believe it helps remove toxins and bacteria from the mouth. While some studies suggest potential benefits for oral health, more research is needed.
-
Green Tea: Green tea contains antioxidants with anti-inflammatory properties that might help reduce gum inflammation. Consider incorporating sugar-free green tea into your daily routine.
-
Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel possesses anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Topical application of aloe vera gel to the gums might provide some relief from gum inflammation. However, scientific evidence for its effectiveness is limited.
-
Cranberries: Cranberries contain compounds that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the teeth. While cranberry juice might offer some benefits, more research is needed to determine its effectiveness for gum disease specifically.
-
Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria that can promote a healthy balance of oral flora. Early research suggests that probiotics might be beneficial for gum health, but more robust studies are needed to confirm their efficacy.
Important Considerations for Complementary Therapies:
- Limited Scientific Evidence: While some of these therapies hold promise, the scientific evidence for their effectiveness in treating gum disease is often limited. More research is needed to establish their definitive role.
- Not a Replacement for Professional Care: These therapies should never be used as a replacement for professional dental care. They can be considered as complementary approaches alongside your dentist’s treatment plan.
- Consult Your Dentist: Before starting any complementary therapy, discuss it with your dentist to ensure it doesn’t interfere with your dental treatment plan and is safe for you.
Maintaining a Healthy Mouth Starts with You:
Gum disease is a preventable and treatable condition. Here’s a final emphasis on the importance of a proactive approach to oral health:
- Develop a Consistent Oral Hygiene Routine: Brushing twice daily with proper technique, flossing daily, and using tongue cleaners are essential for removing plaque and preventing its buildup.
- Schedule Regular Dental Checkups: Regular dental checkups allow your dentist to identify and address gum disease early on, preventing complications.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients promotes overall oral health. Limit sugary foods and processed carbohydrates that contribute to plaque formation.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on oral health. Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga to promote overall well-being.
Conclusion:
While maintaining good oral hygiene habits is crucial for gum health, completely curing gum disease solely at home isn’t recommended. Professional dental care is essential for proper diagnosis, treatment, and long-term gum health management. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing gum disease from progressing and potentially causing tooth loss. Utilize the information provided to support your gum health alongside seeking professional dental care for optimal oral well-being.